Want an SBC that can run heavy AI inference, host fast NVMe storage, and act as a compact workstation, all on one board?
The upcoming Orange Pi 6 Plus ARM development board marks a major step forward for the Orange Pi team, introducing a powerful new development board built around a 12-core ARM processor. Designed to appeal to both hobbyists and industry professionals, it brings a significant boost in performance and flexibility, ideal for modern DIY builds and embedded system projects. A key highlight is its integrated 30-TOPS NPU, which positions the board as a strong choice for AI-driven edge computing.
What further sets the Orange Pi 6 Plus apart is its advanced SoC engineered by CIX Technology, an emerging semiconductor company in China. Although not yet widely known, CIX is backed by a highly experienced engineering team with over two decades of expertise, making the company and its innovations, worth watching closely as it gains momentum in the industry.
Why the OrangePi 6 Plus Matters?
The OrangePi 6 Plus packs a 12-core CIX family SoC, LPDDR5 memory up to 64GB, dual M.2 NVMe slots, and a dedicated NPU rated in vendor materials up to 45 TOPS (system / combined figures). That hardware places it in the class of ARM SBC for AI edge computing designed for On-device AI, compact workstations, and multi-camera/edge-server use cases.
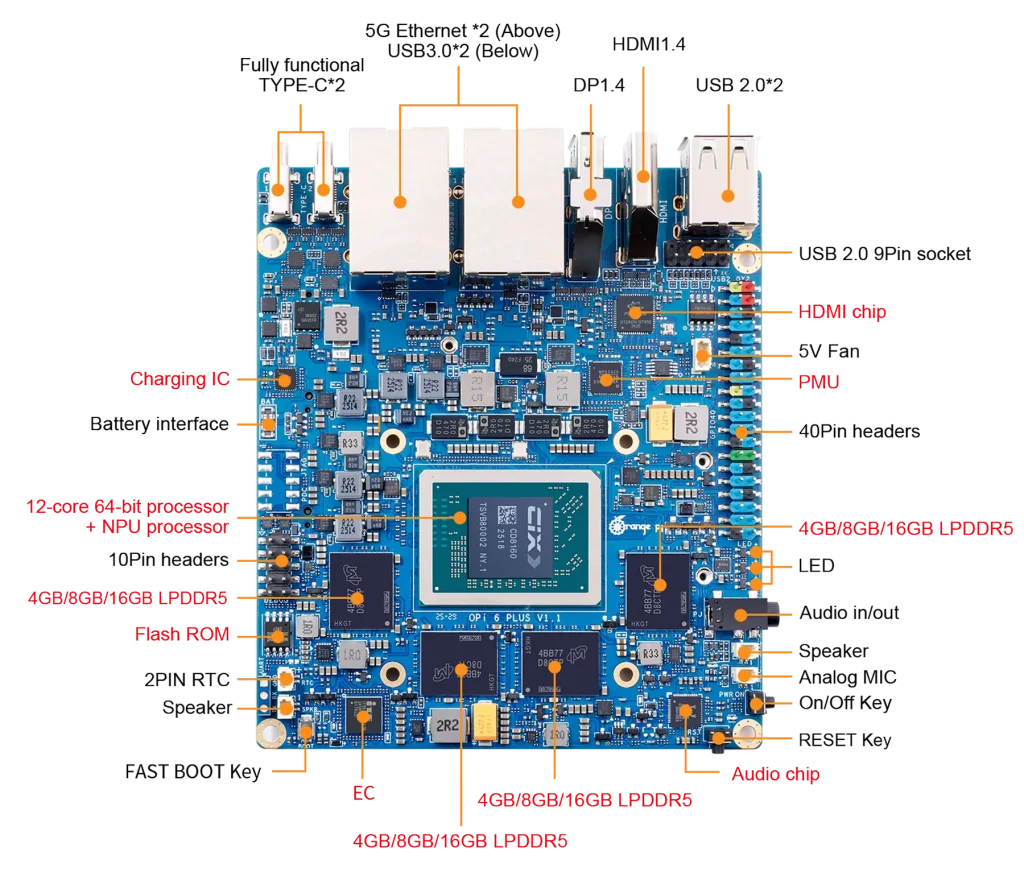
Orange Pi 6 Plus ARM Development Board Hardware Overview
|
CPU |
12-core 64-bit processor |
|
NPU |
28.8Tops |
|
GPU |
Integrated graphics processor |
|
Combined Computing Power |
45TOPS(CPU+NPU+GPU) |
|
RAM |
LPDDR5: 128-bit x 32;16GB/32GB /64GB |
|
Storage Expansion |
• SPI FLASH: 64Mbit |
|
Wi-Fi Module |
M.2 KEY-E socket |
|
PCIE Ethernet |
5G Ethernet*2 |
|
USB |
• USB 3.0 HOST *2 |
|
Camera Interface |
2*4-lane MIPI CSI camera interface |
|
Display Interface |
• 1*DP1.4 4K@120HZ |
|
Audio |
3.5mm headphone jack audio input/output, speakers*2, analog MIC*1 |
|
TYPE-C Port Power Supply |
Type-C PD 20V IN*2, standard 100W |
|
Expansion Interface |
40-pin function expansion interface, supporting the following interface types: |
|
Indicator Light |
Power-on indicator, system indicator, battery charging indicator |
|
Button |
1* Power button, 1* BOOT button, 1* RESET button |
|
Fan Interface |
1* Fan connector with PWM control |
|
Reserved Interface |
Board-to-board battery connector; 2-pin RTC connector |
|
Power Adapter |
Type-C PD 20V input, standard 100W |
|
Operating System |
Debian, Ubuntu, Android, Windows, ROS2 |
|
Appearance Dimensions |
115*100mm |
|
Weight |
132g |
Core Silicon (SoC)
- SoC family: CIX CD8180 / CD8160 series (CIX / CD8xxx family).
- CPU: 12-core ARM64 configuration (mix of newer high-performance cores + efficiency cores) designed for high single-thread and multi-thread throughput.
Memory & Storage
- RAM: LPDDR5 (128-bit bus), available in SKU options such as 16 GB, 32 GB, and up to 64 GB. LPDDR5 delivers much higher bandwidth than LPDDR4(X), which benefits GPU/NPU and data-intensive workloads.
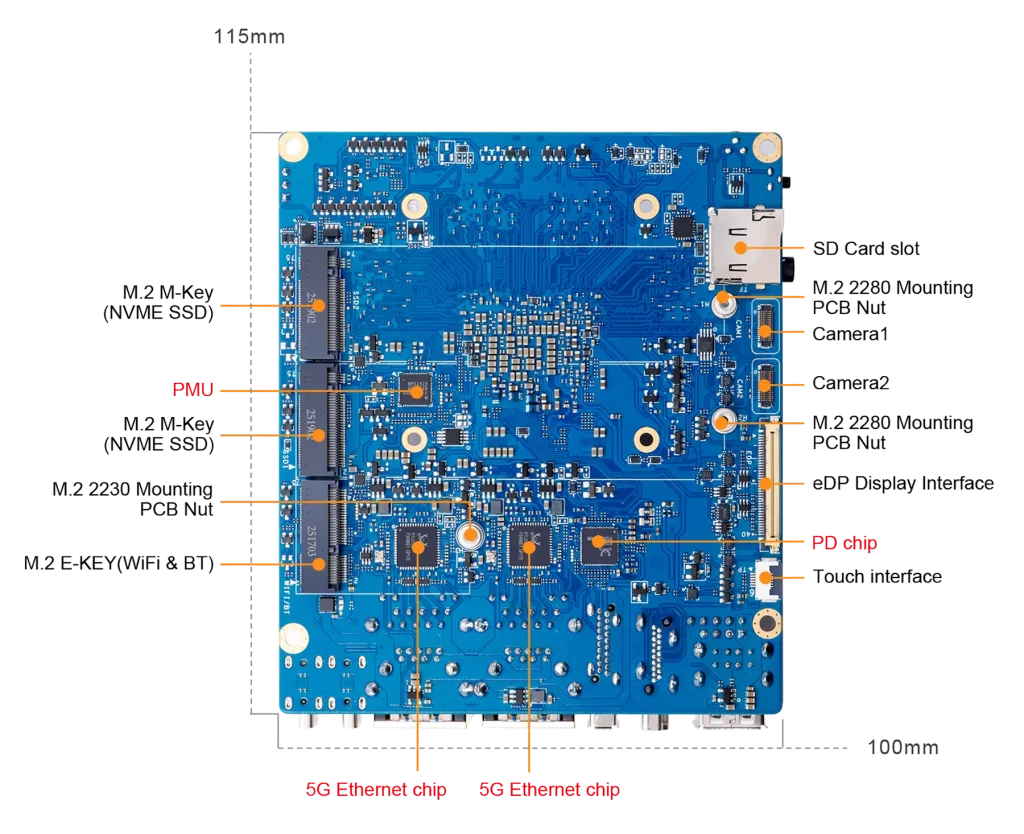
- Storage: Two M.2 2280 NVMe slots (PCIe) on many SKUs plus eMMC socket and microSD for flexible system storage and ultra-fast SSD options.
AI & GPU
- NPU: Vendor and press materials advertise up to ~30 TOPS for the NPU alone and system figures up to ~45 TOPS in combined metrics (NPU + GPU + DSP), depending on precision and measurement. This is a meaningful step for on-device AI workloads.
- GPU: Modern Arm-class GPU (Immortalis-class on related chips reported) with modern API support (Vulkan/OpenGL ES), making it suitable for GPU-accelerated compute and desktop composition.
The glmark2 benchmark is a valuable tool for evaluating OpenGL ES 2.0 performance on systems running the Wayland display server. It measures how well a device handles essential graphics workloads, including vertex processing, texture management, and shader execution. This makes it especially useful for developers optimizing graphics performance on embedded systems and Linux-based devices. In our hands-on testing, the Orange Pi 6 Plus delivered impressive results, achieving a glmark2-wayland score of 1105 and an exceptional 5851 in the glmark2-es2-wayland test—clear indicators of its strong GPU capabilities.
I/O and Networking
- Ethernet: Options include multi-gigabit connectivity, vendor pages and previews cite Dual 5GbE on some configurations (great for NAS, multi-stream AI data ingestion and low-latency networks).
- USB & Display: The board offers an impressive range of display output options, including HDMI, DisplayPort, USB-C with DP Alt Mode, and eDP—capable of delivering stunning 4K at 120Hz visuals via DisplayPort.
- Other: 40-pin GPIO, fan connector, RTC header, and expansion slots common to Orange Pi family boards.
OrangePi 6 Plus Benchmark Technical Deep Dive (What these specs mean in practice?)
CPU Design & Performance Expectations
The CIX CD8180 is a high-performance 12-core Armv9.2 processor developed by CIX Technology, a Chinese semiconductor company specializing in AI-focused and edge-computing SoCs. It uses a tri-cluster architecture featuring 4 Cortex-A720 “Big” cores (up to 2.8 GHz), 4 Cortex-A720 “Medium” cores (up to 2.4 GHz), and 4 Cortex-A520 “LITTLE” cores (up to 1.8 GHz), providing an efficient balance between performance and power consumption. The chip includes an Arm Immortalis-G720 MC10 GPU with hardware ray tracing and support for Vulkan 1.3, OpenGL ES 3.2, and OpenCL 3.0. Complementing this is a robust 30-TOPS NPU that supports INT4/8/16, FP16, and TF32 precision, making it highly capable for modern AI workloads.
Edge AI computing SBC Note: Benchmarks published in early hands-on previews and community tests show the board is competitive with other top SBCs for single-thread tasks and often excels in multi-threaded workloads when paired with adequate cooling.
Power Consumption
Idle Power Consumption: The board typically uses 5–7 watts when idle, depending on attached peripherals and background activity.
Moderate Workloads: During everyday tasks—such as web browsing or light AI inference—power usage generally falls between 10–15 watts.
Peak Usage: Under maximum CPU, GPU, and NPU load, especially when running NVMe storage or dual Ethernet, consumption can reach 18–20 watts.
Power Requirements: The Orange Pi 6 Plus is powered via USB-C Power Delivery, and a 20W or higher power adapter is recommended to ensure stable performance.
Memory Bandwidth & Why LPDDR5 Matters?
LPDDR5 increases memory bandwidth and reduces latency vs LPDDR4(X). For workloads that shuttle large tensors or frames between NPU/GPU/CPU (e.g., vision pipelines, LLM embeddings), that bandwidth is often the bottleneck — so LPDDR5 gives measurable gains in throughput and reduced stalls. If you plan to run large models or many parallel vision streams, the high RAM ceiling (up to 64 GB) is a standout feature.
NPU and On-device AI: Realistic Expectations
Marketing TOPS numbers vary depending on precision (INT4/8, FP16, etc.) and whether the figure is NPU alone or a combined system value. Practical considerations:
- Model format & conversion required: Many models need quantization (INT8/INT4) or conversion to vendor runtimes to hit peak NPU throughput. Community tools and runtimes are evolving.
- Use cases: The board can handle object detection, segmentation, and many smaller transformer models for embeddings or low-latency responses on the edge. For very large LLMs, the limiting factors are model size and runtime support rather than raw TOPS alone.
The Orange Pi 6 Plus features a powerful NPU capable of delivering 30 TOPS, dramatically improving both AI development and on-device deployment. It supports a wide range of mainstream AI models, making it well-suited for edge-based generative AI workloads such as chatbots, coding assistants, and real-time intelligent applications.
In terms of AI capability, the board is often compared to the AMD Ryzen AI 9 HX 370, as both platforms reach up to 45 TOPS when leveraging their combined AI engines—allowing advanced models to run locally with high efficiency. Paired with the Arm Immortalis-G720 MC10 GPU, the Orange Pi 6 Plus also provides high-end graphics performance, including 8K video decoding and hardware-accelerated ray tracing, making it an excellent choice for demanding multimedia and graphics-intensive tasks.
Storage and I/O in Real Deployments
Dual NVMe slots let you build compact, high-IOPS NAS/DB nodes or host databases and container images locally with low latency. Combined with multi-gigabit Ethernet, the 6 Plus can operate as a small, fast edge server or inference appliance. This combination of NVMe + multi-GbE is rare on SBCs and a key differentiator vs older Orange Pi models and many competitors.
Software & Community (Maturity and Compatibility)
- OS support: Early images for Debian/Ubuntu and Android are being published; community ports and kernel work are ongoing. Expect active community development but anticipate some early-adopter quirks (driver refinements, firmware updates) while mainline support grows.
- AI toolchain: Tooling to convert and optimize models for the NPU will be necessary. Users on community forums report early experiments with model conversion and runtime integration; expect growing documentation in the months after launch.
ARM SBC for AI edge computing Typical Use Cases
Great fit for:
- Edge AI developers (real-time vision, inference appliances) who need local NPU acceleration.
- Makers building compact servers, NVMe-backed storage appliances, or multi-camera robotics.
- Developers wanting a powerful Linux desktop SBC for compiling code, running containers, or lightweight virtualization.
Not the best fit for:
- Users who need a plug-and-play, extensively battle-tested platform without tinkering — early adopters will face software polishing steps.
ARM Dev Board for AI Real-world Notes & Early reports
- Early reviewers and community testers report that the board performs well in synthetic and some real workloads, but sustained multi-core/NPU throughput benefits from active cooling.
- The NPU’s real-world effectiveness depends on runtime support and model conversion — which is improving but still maturing in community toolchains.
OrangePi6 Plus Pros & Cons
Pros
- High AI compute potential: Vendor/system figures advertise up to 45 TOPS (combined); NPU alone commonly cited around 30 TOPS — great for edge inference.
- Large, fast RAM: LPDDR5 support and high SKUs up to 64 GB enable large models, heavy multitasking and memory-hungry workloads.
- Dual NVMe + multi-GbE: Two M.2 2280 NVMe slots and dual 5 GbE options enable compact, high-IOPS storage solutions and fast networked inference.
- Modern GPU & display I/O: Modern GPU APIs (Vulkan, OpenGL ES) and robust display outputs — good for GPU-accelerated tasks and desktop use.
- Solid CPU core count: 12 cores give strong parallel compute for server-style and workstation tasks.
Cons
- Early software maturity: As a new platform with a newer SoC family, mainline kernel support, optimized runtimes, and community docs are still arriving, expect early-adopter work.
- Power & thermal demands: For best sustained performance on CPU and NPU, active cooling (fan + heatsink) is recommended. Expect higher power draw under load.
- Marketing TOPS vs real throughput: TOPS numbers are useful but depend heavily on precision, model format, and runtime real gains require model optimization.
- Price & availability variability: Advanced SKUs (large RAM, bundled accessories) carry a premium and availability may vary by region and seller.
OPi 6 Plus Price?
By the way, The Orange Pi 6 Plus is currently(2025) priced in the $199–$224 range across major global marketplaces, depending on the seller, memory configuration, and regional availability. This pricing positions it as a powerful yet cost-effective alternative to premium single-board computers, offering strong value for performance-focused buyers.
Real-World Performance Comparison: Orange Pi 6 Plus vs Raspberry Pi 5
1. Performance (CPU & Throughput)
Orange Pi 6 Plus
-
The 6 Plus uses a 12-core CIX (CD8180 / CD8160) SoC with a mix of Cortex-A720 and A520 cores.
-
According to CNX Software, it’s built on a 6 nm process and offers high-performance CPU, GPU, and NPU.
-
Graphics benchmarks: according to AndroidPimp, glmark2-wayland score is ~1,105, and glmark2-es2-wayland is ~5,851 — indicating strong GPU performance.
-
AI performance: up to 45 TOPS total (CPU + GPU + NPU) for model inference.
Raspberry Pi 5
-
The Pi 5 uses a Broadcom BCM2712 CPU with 4× Cortex-A76 cores @ 2.4 GHz.
-
In a real review, CNX-Software measured memory bandwidth, throughput, and other benchmarks using their sbc-bench suite.
-
No dedicated high-TOPS NPU on Pi 5 — it’s not designed for heavy on-device AI inference.
Summary point: The Orange Pi 6 Plus has significantly higher raw compute potential, especially for multi-threaded and AI workloads. The Pi 5 is more traditional compute-oriented and less focused on AI inference.
2. AI / Inference Workloads
Orange Pi 6 Plus
-
The NPU provides up to 30 TOPS, and combined with GPU + CPU, total AI throughput is claimed up to 45 TOPS.
-
Supported precisions: INT4, INT8, INT16, FP16, BF16, TF32.
-
With this much AI power, it’s suitable for on-device inference of vision models, LLM embeddings, or other AI workloads that require local compute.
Raspberry Pi 5
-
The Pi 5 does not have a dedicated high-performance NPU. Inference on Pi 5 is therefore limited to CPU/GPU or external accelerators.
-
There are academic experiments: for example, a paper deployed a quantized YOLOv4-Tiny model on the Pi 5 and measured inference times and power.
-
Because of this, Pi 5 is more suited for lightweight AI use or as a development platform when using external AI hardware.
Summary point: For serious on-device AI inference, the 6 Plus has a clear advantage. The Pi 5 is more limited without external AI acceleration.
3. Power Consumption & Efficiency
Orange Pi 6 Plus
-
According to AndroidPimp’s hardware overview, idle power draw is around 5–7 W, depending on attached peripherals.
-
Under moderate load (e.g., light inference or SSD usage), power consumption can go up to 10–15 W.
-
Under full load (CPU + NPU + NVMe + network), peak power can reach 18–20 W, per the same source.
-
Requires a beefy power supply: the board supports USB-C PD, and a 20 V or similarly powerful adapter is recommended.
Raspberry Pi 5
-
In the CNX-Software review, idle power consumption is quite low: ~3.0 W (headless) to ~3.6 W (with peripherals).
-
Under a 4-core stress test, Pi 5’s measured power consumption was around 8.8 W.
-
In a heavier combined workload (4K video + external SSD + stress test), it can go up to ~16.8 W per tests.
-
Pi 5 runs hot: Tom’s Hardware measured thermal throttling — under load, it reached ~86.7 °C and the CPU scaled down to reduce temperature.
Summary point: The Pi 5 is very power efficient when idle but can draw significant power under heavy load; the 6 Plus draws more overall but gives far greater performance per watt when doing AI or data-heavy workloads.
4. Real-World Use Case Implications
For Edge AI / Inference / Robotics
-
With high AI throughput (45 TOPS), the Orange Pi 6 Plus is very well-suited for on-device AI, robotics, computer vision, and applications that benefit from running models locally rather than relying on the cloud.
-
Its power draw under load is higher, so use in battery-powered or power-constrained environments requires careful design (good PSU, possibly power management).
-
The dual NVMe slots also allow for very fast local storage of models and data.
For Maker / General-Purpose Use
-
The Raspberry Pi 5 excels in general development, education, media projects, and typical maker applications.
-
For AI on Pi 5, you’d likely use quantized models or external accelerators (e.g., USB NPUs) because the built-in CPU/GPU capacity is limited.
-
The Pi 5’s lower idle power makes it ideal for always-on tasks, small servers, IoT gateways, or retro computing where efficiency is more important than raw AI performance.
See also: OrangePi 6 Plus vs OrangePi 5 Plus: Want a faster SBC or one built for AI?

Verdict on Performance + AI + Power
-
Compute & AI: The Orange Pi 6 Plus wins hands-down for raw compute power and on-device AI inference. Its 12-core CPU, powerful NPU, and high memory bandwidth make it a top choice for AI-heavy workflows.
-
Energy Efficiency (idle): The Raspberry Pi 5 is more efficient when doing lighter tasks , great for low-power projects.
-
Power Budget for AI Projects: If you’re building an AI edge device or local inference box, the Orange Pi 6 Plus is very compelling , just plan for a strong power supply and good cooling.
-
Ease of Use & Ecosystem: The Pi 5 benefits from Raspberry Pi’s mature ecosystem, whereas the 6 Plus may require more work to fully leverage its AI capabilities.
OrangePi 6Plus : 45 Tops of Combined AI computing power!
Introducing OrangePi 6Plus with with a 12-core 64-bit CPU, and delivers up to 45 TOPS combined AI.
Conclusion:
If your next project needs on-device AI acceleration, high memory capacity, NVMe storage, and multi-gigabit networking in a single SBC, the OrangePi 6 Plus is one of the most capable boards available today. It’s particularly compelling for edge-AI deployments, robotics, and compact NAS/edge-server use cases.
If you prefer maximum out-of-the-box software stability with long community history, you may prefer to wait a short while for the platform to mature , but if you’re comfortable with early-adopter tasks and want top-tier hardware on a single board, the 6 Plus is worth exploring.
Discover the newest Orange Pi boards and compatible accessories designed for AI, IoT, and edge-computing applications. Explore our handpicked selection to find the right option for your next project in the OrangePi products in the Siqma Store.
FAQs:
-
What makes the Orange Pi 6 Plus different from previous Orange Pi models?
The Orange Pi 6 Plus introduces a significant leap in performance thanks to its 12-core Armv9.2 CPU, Immortalis-G720 MC10 GPU, and 30-TOPS NPU, none of which were available in earlier models. It also offers LPDDR5 RAM up to 64GB, dual NVMe SSD slots, and dual 5GbE Ethernet, making it suitable for high-end AI workloads, edge computing, and small-form-factor servers. This is the most powerful and AI-focused Orange Pi board to date.
-
Can the Orange Pi 6 Plus run large AI models locally without cloud access?
Yes. With its 30-TOPS NPU and high-bandwidth LPDDR5 memory, the Orange Pi 6 Plus is designed for on-device AI processing. It can efficiently run quantized LLMs, computer vision models, and generative AI pipelines without relying on cloud services. This allows for lower latency, improved privacy, and real-time inference—ideal for robotics, automation, and offline AI assistants.
-
How does the GPU on the Orange Pi 6 Plus compare to typical ARM SBC GPUs?
The board’s Arm Immortalis-G720 MC10 GPU is far more advanced than the GPUs found in most Raspberry Pi or older Orange Pi boards. It supports hardware-accelerated ray tracing, 8K video decoding, and modern APIs such as Vulkan 1.3 and OpenGL ES 3.2. This makes it capable of handling demanding 3D workloads, high-resolution media playback, and GPU-accelerated compute tasks.
-
Can Orange Pi6 Plus handle desktop or multimedia tasks?
Yes! The OrangePi 6 Plus is powerful enough to work like a small desktop computer. With its fast CPU, capable GPU, and plenty of RAM, it can smoothly handle web browsing, office work, videos, and even multi-monitor setups. It’s a solid choice if you want a compact board that feels fast in everyday use.
Sources & further reading:
Basic specs and official info: Orange Pi product page. orangepi.org
Hands-on press and initial pricing: CNX-Software.com
Technical coverage & NPU detail: Golem.de